Logging
Logging#
We will take a look at the available options for logging in OpenShift Dedicated (OSD). As OSD 4 does not come preconfigured with a logging solution, we can easily set one up. In this section review the install proceedure for the EFK (Elasticsearch, Fluentd and Kibana) stack (via Operators), then we will take a look at two methods with which one can view their logs. First, we will look at the logs directly through the pod using oc logs. Second, we will use Kibana to search our logs.
The cluster logging components are based upon Elasticsearch, Fluentd, and Kibana (EFK). The collector, Fluentd, is deployed to each node in the OpenShift Dedicated cluster. It collects application logs and writes them to Elasticsearch (ES). Kibana is the centralized, web UI where users and administrators can create rich visualizations and dashboards with the aggregated data.
Learn more about logging on OSD 4 here: https://docs.openshift.com/dedicated/4/logging/cluster-logging.html
Output data to the streams/logs#
1. Output a message to stdout#
Click on the Home menu item and then click in the message box for "Log Message (stdout)" and write any message you want to output to the stdout stream. You can try "All is well!". Then click "Send Message".

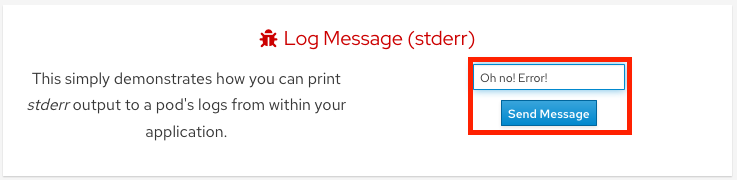
2. Output a message to stderr#
Click in the message box for "Log Message (stderr)" and write any message you want to output to the stderr stream. You can try "Oh no! Error!". Then click "Send Message".
Viewing pod logs#
3. Retrieve front end pod name#
Go to the CLI and enter the following command to retrieve the name of your frontend pod which we will use to view the pod logs:
$ oc get pods -o name
pod/ostoy-frontend-679cb85695-5cn7x
pod/ostoy-microservice-86b4c6f559-p594d
So the pod name in this case is ostoy-frontend-679cb85695-5cn7x.
4. Retrieve the logs from the pod#
Run oc logs ostoy-frontend-679cb85695-5cn7x and you should see your messages:
$ oc logs ostoy-frontend-679cb85695-5cn7x
[...]
ostoy-frontend-679cb85695-5cn7x: server starting on port 8080
Redirecting to /home
stdout: All is well!
stderr: Oh no! Error!
You should see both the stdout and stderr messages.
Using Kibana to search logs#
5. View the Kibana console#
In the OpenShift Webconsole click on Monitoring > Logging in the left menu.
Open up a new browser tab and go to https://logs.<cluster name>.openshfit.com to access the Kibana console. Ensure the correct project is selected. In the beginning of this lab we created the ostoy project. So select the one that begins with project.ostoy....
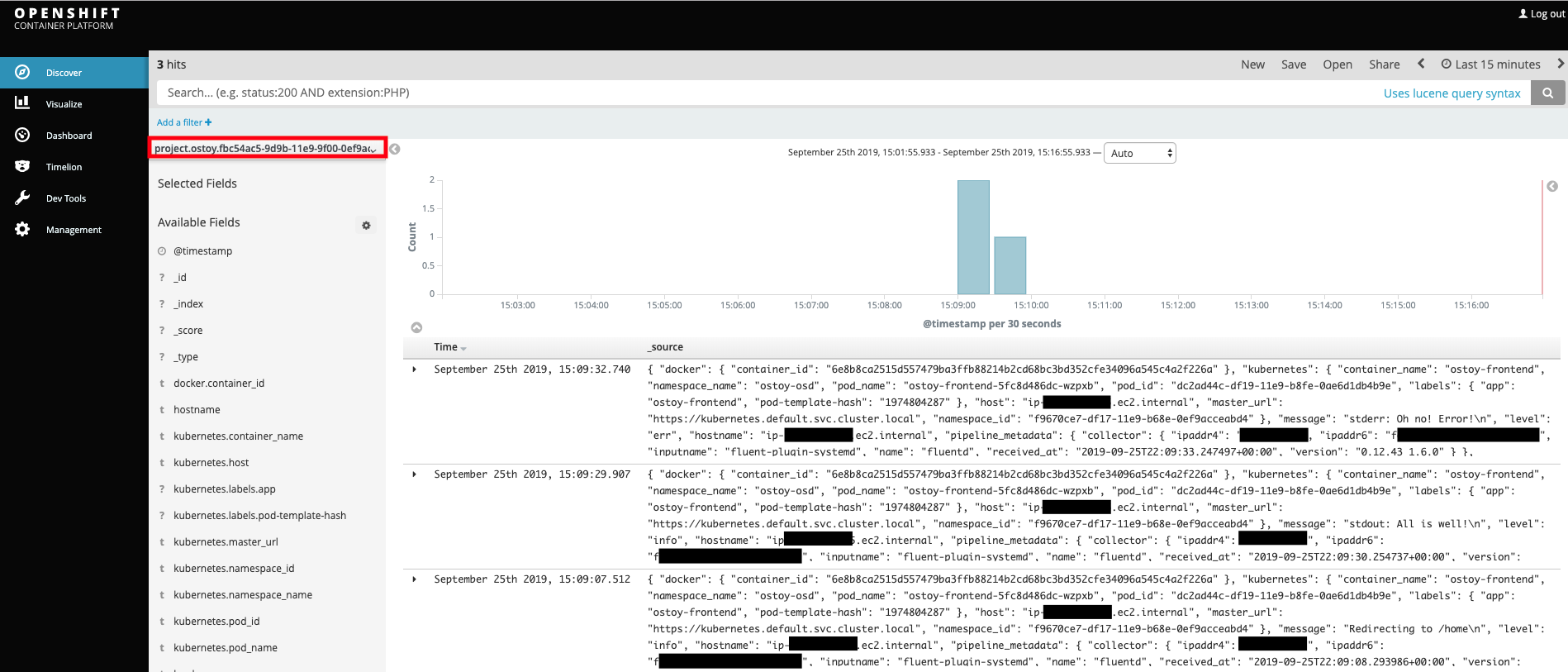
6. Familiarization with the data#
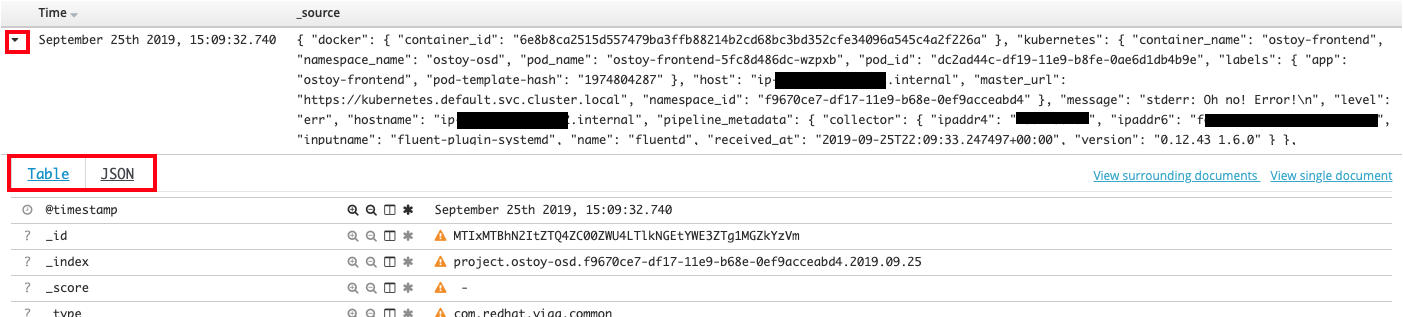
In the main part of the console you should see three entries. These will contain what we saw in the above section (viewing through the pods). You will see the stdout and stderr messages that we inputted earlier (though you may not see it right away as we might have to filter for it). In addition to the log output you will see information about each entry. You can see things like: - namespace name - pod name - host ip address - timestamp - log level - message
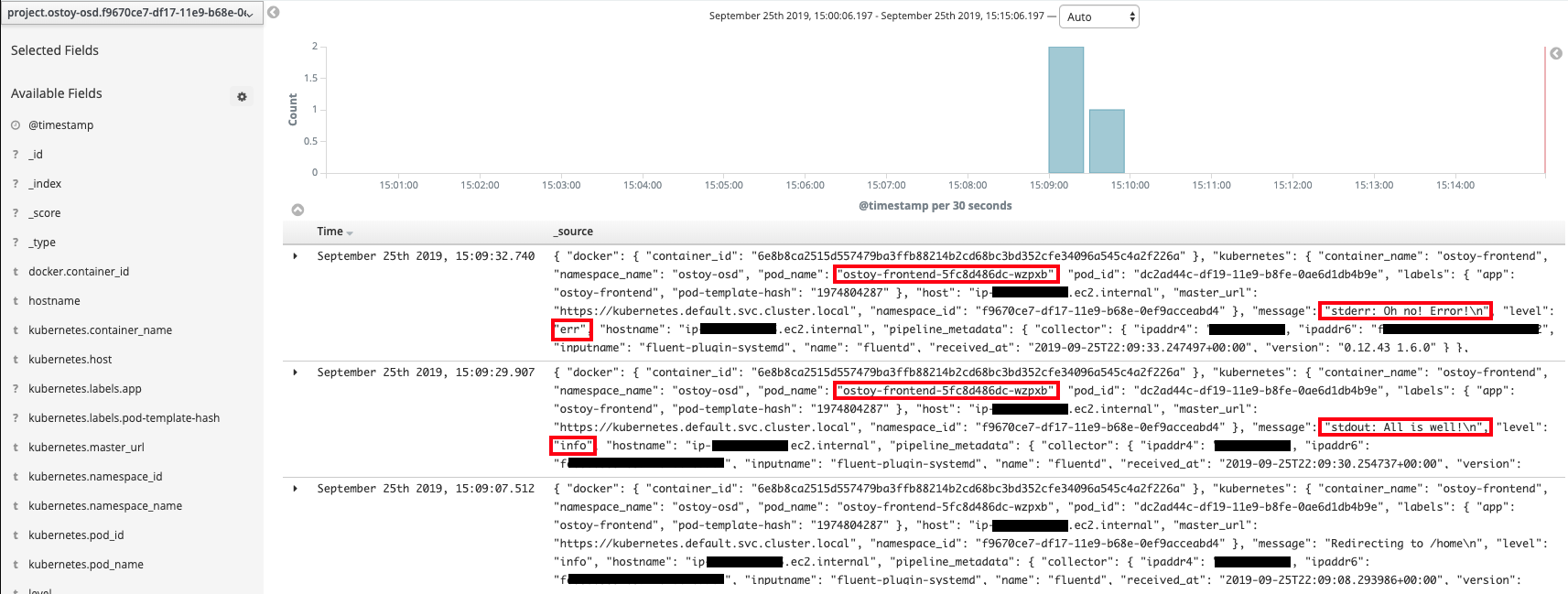
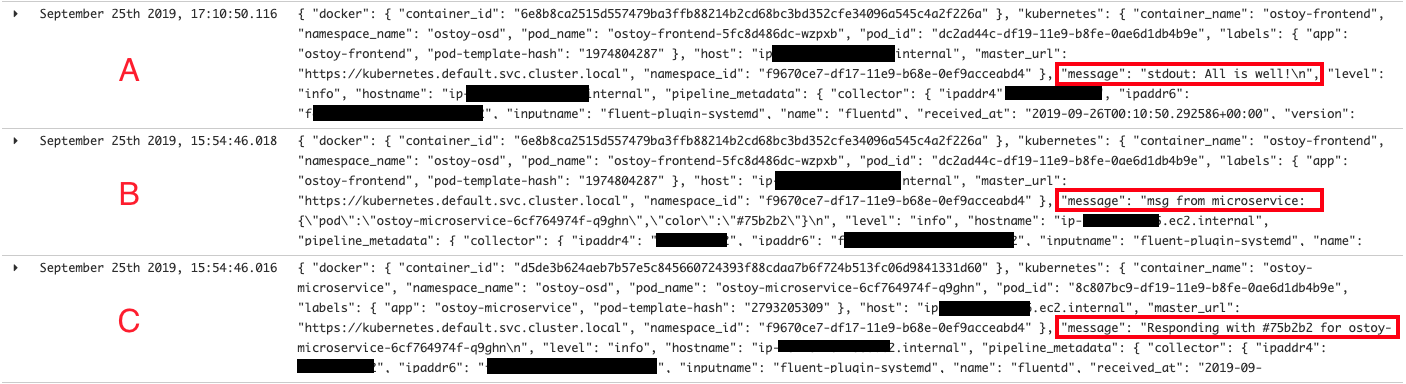
You will also see that there is data from multiple sources and multiple messages. In the image below you can see that
- A) shows the message we outputted to the stdout
- B) shows what our frontend pod received from the microservice (which pod sent it and what color was sent)
- C) shows what color the microservice pod is responding with
Furthermore, if you wanted to see the data in tabular format or in JSON format you can click on the twisty-tie on the left of the row.
6. Filtering Results#
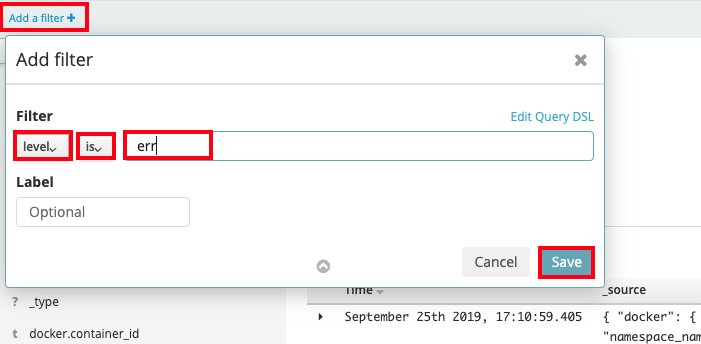
Let's look for any errors encountered in our app. Since we have many log entries (most from the previous networking section) we may need to filter to make it easier to find the errors. To find the error message we outputted to stderr lets create a filter.
- Click on "Add a filter+" under the search bar on the upper left.
- For "Fields..." select (or type) "level"
- For "Operators" select "is"
- In "Value..." type in "err"
- Click "Save"
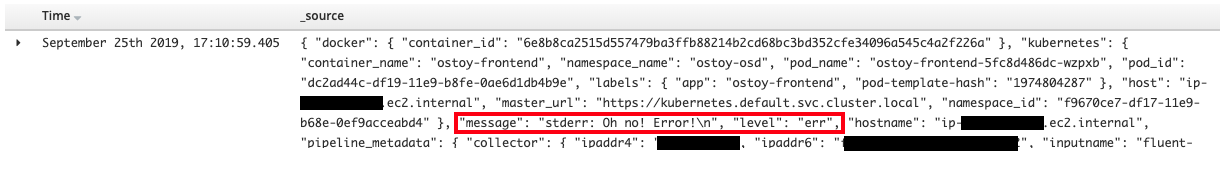
You should see now only one row is returned that contains our error message.
NOTE: If nothing is returned, depending on how much time has elapsed since you've outputted the messages to the stdout and stderr streams you may need to set the proper time frame for the filter. If you are following this lab consistently then the default should be fine. Otherwise, in the Kibana console click on the top right where it should say "Last 15 minutes" and click on "Quick" then "Last 1 hour" (though adjust to your situation as needed).